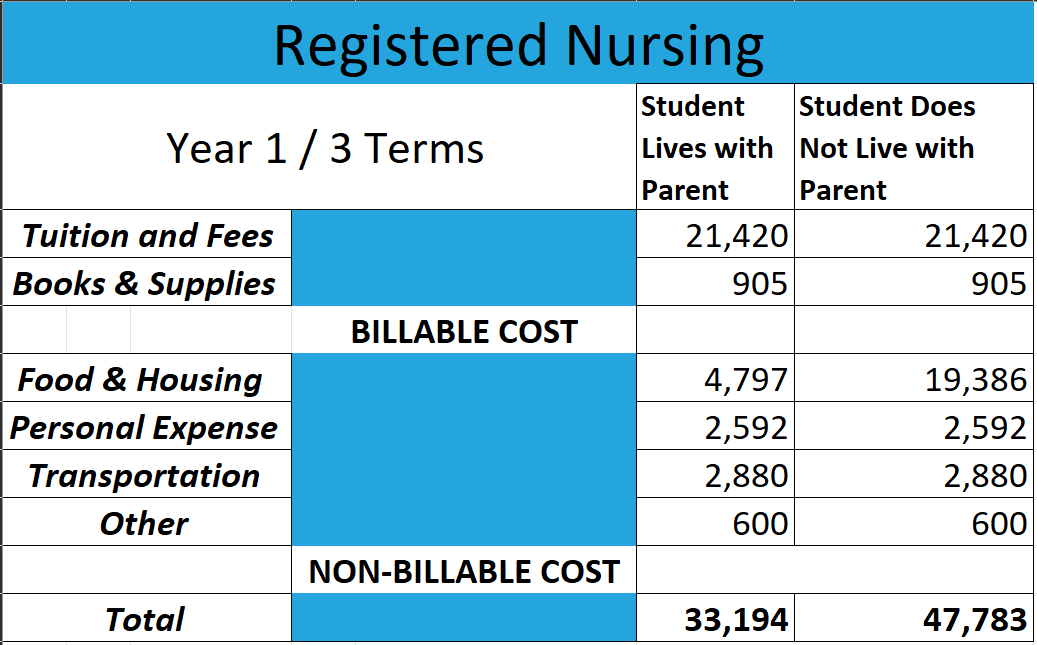
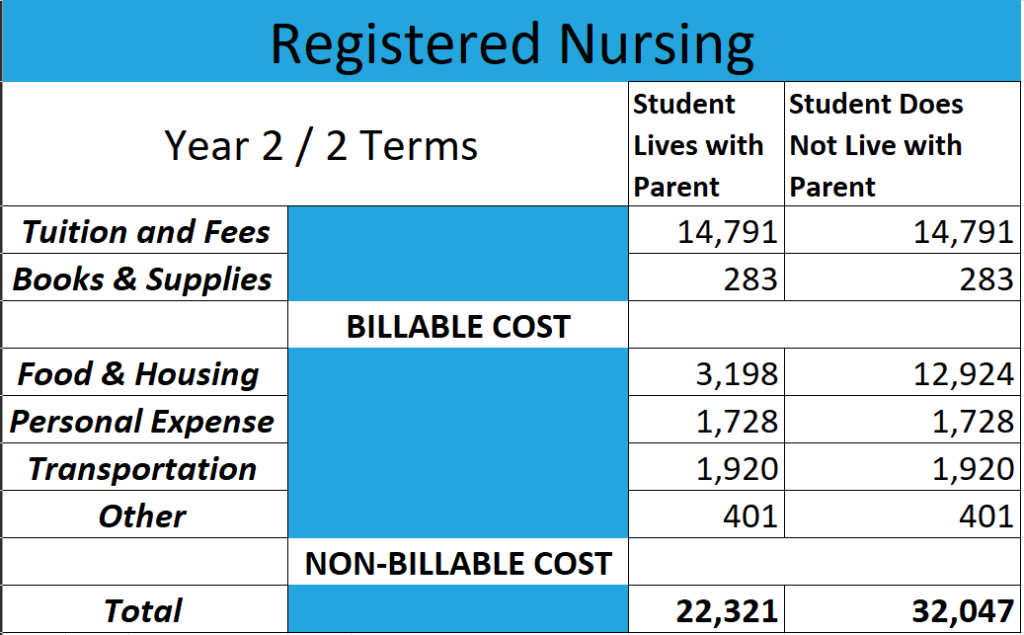
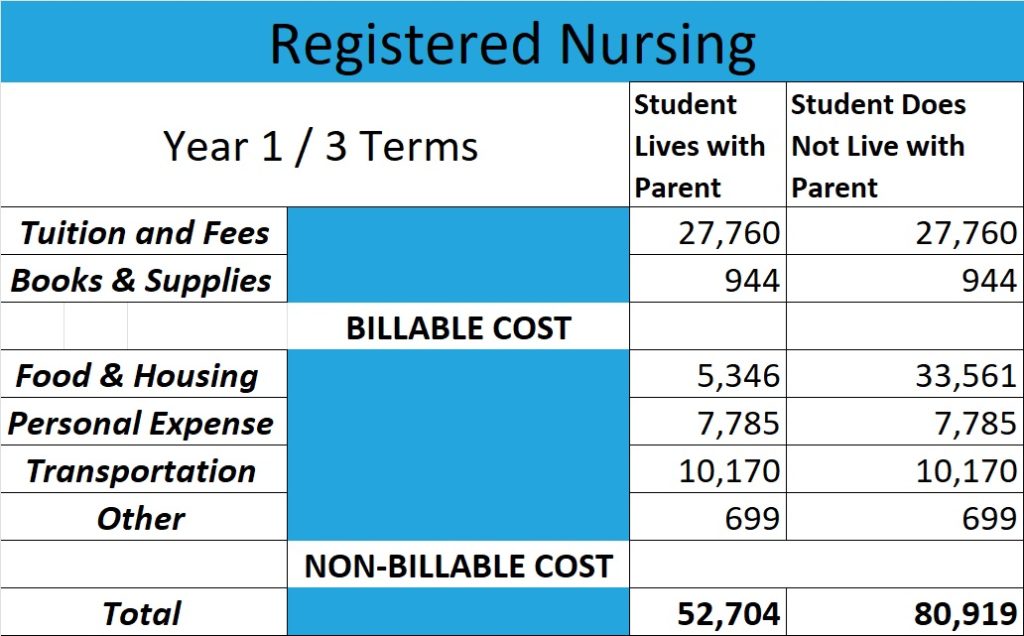
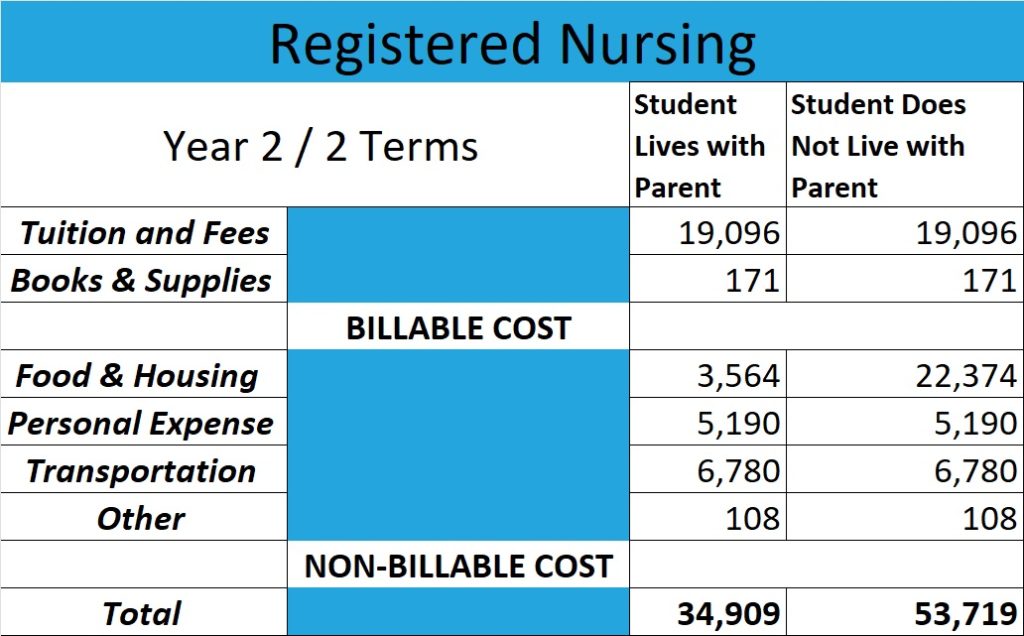
A practical nurse (PN) and a registered nurse (RN) are both healthcare professionals, but there are some key differences between the two—they have different levels of education, training, and responsibilities. A PN typically has a shorter education and training than an RN. A practical nurse is educated and trained to perform routine, standardized tasks under the supervision of an RN or a physician. They may care for patients in hospitals, long-term care facilities, or homes, and their responsibilities include administering medication, monitoring vital signs, and providing basic bedside care. A registered nurse, on the other hand, has a higher education and training level. An RN typically has a college degree in nursing and must pass a national licensure examination to practice. RNs have a more advanced understanding of nursing theory and the nursing process and are responsible for more complex patient care tasks. They may also have supervisory responsibilities over practical nurses and other healthcare workers. RNs may practice in a wide range of healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, schools, and patient homes. To sum up, PNs are more focused on hands-on care and implement care plans set up by RNs and physicians, while RNs have a more advanced understanding of nursing theory, are responsible for more complex patient care tasks, and have a supervisory role over LPNs and other healthcare staff.