Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide, characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways. Managing it typically involves using medications to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
However, many seek complementary therapies to enhance their treatment plans and improve overall well-being. One such therapy is acupuncture, an ancient practice rooted in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).
So, read on as we explore the benefits of acupuncture for asthma relief, highlighting the research and evidence that support its effectiveness as a complementary treatment for those living with asthma.
Benefits of Acupuncture for Asthma
Below, we explore some of the primary benefits of asthma acupuncture, highlighting how this ancient practice can support asthma management and improve overall well-being.
1. Reduces inflammation
Inflammation is a key component of asthma, leading to airway constriction and breathing difficulties. Acupuncture has been shown to reduce inflammation by modulating the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines and promoting anti-inflammatory responses.
When specific acupuncture points are stimulated, they can help regulate the body’s immune response, decreasing the overall inflammatory burden. This reduction in inflammation can lead to fewer asthma symptoms and improved respiratory function. By targeting inflammation directly, acupuncture can be a valuable adjunct to traditional asthma treatments, potentially reducing the need for higher doses of anti-inflammatory medications.
Research supports the anti-inflammatory effects of acupuncture in asthma treatment through multiple mechanisms. Studies have demonstrated that acupuncture can significantly reduce the number of inflammatory cells, such as neutrophils and eosinophils, in both animal models and humans.
For instance, electroacupuncture at specific points like GV 14, BL 13, and ST 36 has been shown to decrease the total cell counts and inflammatory infiltrates in the airways, leading to reduced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation.
Additionally, manual acupuncture at points such as BL 13 and ST 36 has been found to lower the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, and TNF-α, further supporting its role in mitigating the inflammatory response associated with asthma.
2. Improves immune function
Research indicates that acupuncture not only reduces inflammation but also improves overall immune function, which is crucial for managing asthma. Asthma is characterized by adaptive and innate immune responses, and studies emphasize the importance of the innate immune system in asthma pathogenesis.
The innate immune system, consisting of cells and receptors encoded in germline DNA, plays a pivotal role in the body’s initial defense against pathogens. Acupuncture has been shown to modulate these immune responses, potentially enhancing the body’s ability to fight off respiratory infections and allergens that trigger asthma.
Acupuncture can influence the activity of innate immune cells, such as dendritic cells and bronchial epithelial cells, which play significant roles in initiating and regulating immune responses. For instance, dendritic cells, which act as antigen-presenting cells, bridge the innate and adaptive immune systems by capturing and presenting antigens to T cells. Acupuncture has been shown to enhance the maturation and function of these cells, thereby improving the overall immune response.
Additionally, acupuncture can stimulate Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and other innate immune receptors, promoting the production of cytokines that are essential for a balanced immune response. By modulating these pathways, acupuncture helps maintain a healthier immune environment, reducing the likelihood of asthma exacerbations triggered by infections or allergens.
Additionally, acupuncture’s ability to enhance T-lymphocyte activity, including regulatory T cells (Tregs), is particularly beneficial for asthma patients. Tregs are key in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing excessive inflammatory responses. By increasing the number and activity of Tregs, acupuncture helps suppress inappropriate immune reactions, thereby reducing the severity and frequency of asthma attacks. This immunoregulatory effect of acupuncture supports the overall health of asthma patients, leading to fewer complications and faster recovery from respiratory infections.
In essence, acupuncture not only targets the symptoms of asthma but also strengthens the immune system, providing a comprehensive approach to asthma management.
3. Enhances lung function
Lung function is critical to asthma management, as it directly affects the ability to breathe easily and comfortably. Acupuncture has been found to improve lung function by increasing airflow and reducing airway resistance. This is achieved through the relaxation of the bronchial muscles and enhancing respiratory efficiency.
A study on the effects of acupuncture on pulmonary function and heart rate variability in bronchial asthma patients supports these benefits. Patients treated with acupuncture showed significant improvements in several pulmonary function parameters, including forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1), peak expiratory flow (PEF), and various forced expiratory flows (FEF).
These enhancements were notably superior to those observed in patients treated with standard anti-asthma medications. The study concluded that acupuncture’s ability to improve pulmonary function is closely related to its regulatory effects on the autonomic nervous system. It highlights its potential as an effective complementary therapy in asthma management.
Other research also supports the effectiveness of acupuncture in enhancing lung function for individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a condition that shares similarities with asthma. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials have indicated that acupuncture can improve pulmonary ventilation function (FEV1%, FVC), exercise tolerance (6MWD), and quality of life (SGRQ) in patients with COPD.
By stimulating specific acupoints, acupuncture helps regulate the functions of the human viscera, improve the internal environment, and reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, essential factors in COPD and asthma. These findings highlight the potential of acupuncture as a valuable adjunct therapy for improving lung function and overall respiratory health in individuals suffering from obstructive airway diseases.
4. Reduces stress and anxiety
Stress and anxiety are known to exacerbate asthma symptoms and trigger asthma attacks. The mind-body connection is particularly significant in asthma, where emotional stress can lead to physical manifestations of the disease.
Acupuncture is well-known for its ability to reduce stress and anxiety by promoting the release of endorphins and other neurotransmitters that induce relaxation and a sense of well-being. By alleviating stress and anxiety, acupuncture helps break the cycle of stress-induced asthma symptoms, providing a more stable and calm physiological state.
A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials specifically examined the effects of acupuncture on anxiety disorder, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). The analysis, which included twenty RCTs, found that acupuncture was significantly more effective than control conditions in reducing anxiety symptoms, with a standard mean effect size of -0.41. The studies also demonstrated that acupuncture is well-tolerated and safe for treating anxiety disorders.
By integrating acupuncture into their treatment regimen, asthma patients may experience a notable reduction in anxiety, leading to fewer asthma exacerbations and improved overall quality of life.
5. Balances the nervous system
Lastly, dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system can lead to bronchoconstriction and increased mucus production, which are hallmarks of asthma. Acupuncture can balance the autonomic nervous system by modulating the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches. This balance helps to prevent excessive bronchoconstriction and promotes smoother, more efficient breathing.
Emerging evidence supports the efficacy of acupuncture in regulating autonomic nervous system functions, including heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle sympathetic nerve activities. Acupuncture treatment has been shown to activate specific brain regions and modulate neurotransmitter levels, which are important for balancing sympathetic and parasympathetic activities.
By influencing these central mechanisms, acupuncture can effectively alleviate autonomic responses and restore a balanced state in the autonomic nervous system, thereby improving respiratory function and overall well-being in individuals with asthma.
Integrating Acupuncture Into Asthma Management
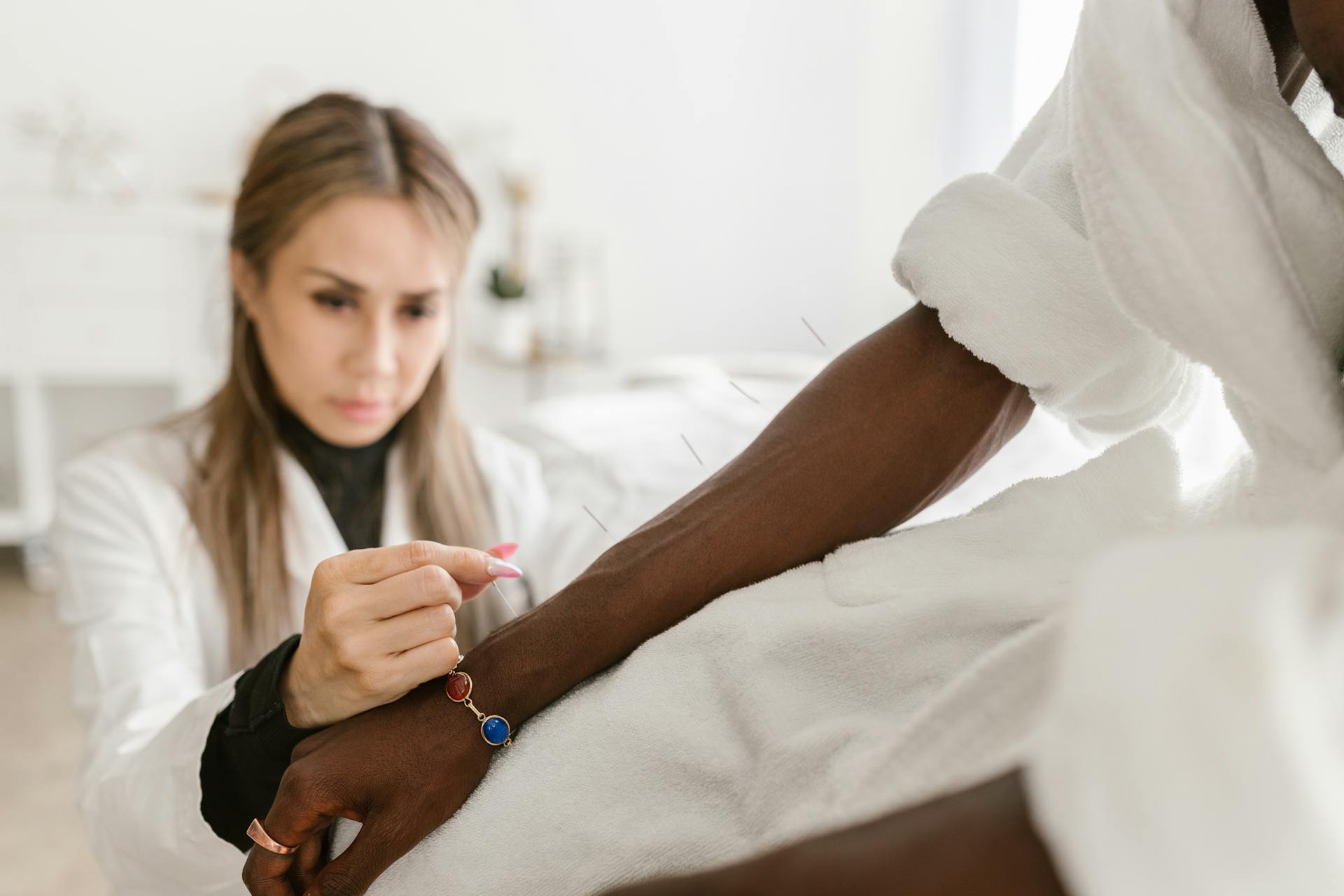

Considering all these benefits, incorporating acupuncture into an asthma treatment plan is a must. It addresses the physical symptoms and supports the emotional and psychological aspects of living with asthma, providing a more balanced and effective approach to managing this condition.
To integrate acupuncture into your asthma management, start by consulting with a licensed acupuncturist experienced in treating respiratory conditions. Share your asthma history and current symptoms to develop a tailored treatment plan.
Initially, acupuncture sessions can be scheduled once or twice a week, gradually reducing frequency as symptoms improve. Coordination with your primary healthcare provider ensures that acupuncture complements your existing treatments, such as medications and inhalers, resulting in a comprehensive strategy for optimal asthma control.
What To Expect During Acupuncture
The practitioner will identify the appropriate acupuncture points to target based on the initial assessment. The patient will then lie comfortably on a treatment table while fine, sterile needles are gently inserted into specific points on the body. These needles may be left in place for about 20 to 40 minutes while the patient relaxes.
Some patients may feel a slight tingling or warmth around the needles, which is a normal sensation. Acupuncture sessions are typically very soothing; many patients feel deeply relaxed and rejuvenated afterward.
Conclusion
Acupuncture offers a multifaceted approach to asthma management, addressing the condition from several angles. By reducing inflammation, improving immune function, enhancing lung function, reducing stress and anxiety, and balancing the nervous system, acupuncture provides a complementary therapy that can support traditional asthma treatments.
While more research is always needed to fully understand the mechanisms and long-term benefits of acupuncture for asthma, existing evidence and patient testimonials highlight its potential as a valuable tool in managing this chronic respiratory condition.
If you or a loved one is seeking a holistic approach to asthma management, consider exploring acupuncture as a complementary therapy. Consult with a licensed acupuncturist to discuss how this ancient practice can be integrated into your treatment plan and take a proactive step toward better respiratory health today.
Book an acupuncture session with one of our qualified acupuncturists, and experience the benefits of acupuncture for asthma firsthand.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many acupuncture sessions are needed for asthma?
The number of acupuncture sessions needed for asthma varies, but typically, patients start with one to two sessions per week, gradually reducing frequency as symptoms improve.
Where are the acupuncture points for asthma?
Common acupressure points for asthma include BL 13 on the back, LU 1 on the chest, and ST 36 on the leg, which are targeted to enhance respiratory function and alleviate symptoms.
Can acupuncture help with shortness of breath?
Yes, acupuncture can help with shortness of breath by stimulating specific acupressure points for asthma, which can improve airflow and reduce bronchoconstriction.